Gladstone NOW: The Campaign Join Us on the Journey✕

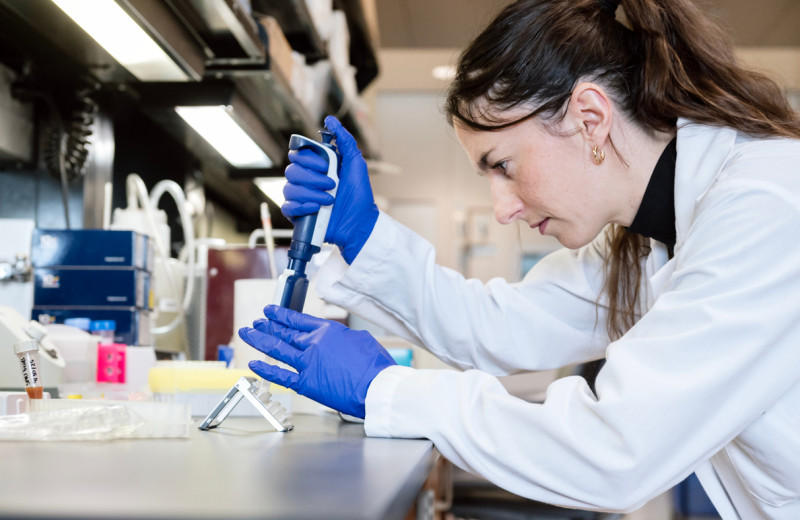
A team of researchers, including Abdullah Syed (left) and Alison Ciling (right), used virus-like particles to identify which parts of the SARS-CoV-2 virus are responsible for its increased infectivity and spread.
As the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 spread rapidly around the globe earlier this year, researchers at Gladstone Institutes, UC Berkeley, and the Innovative Genomics Institute used virus-like particles to identify which parts of the virus are responsible for its increased infectivity and spread.
They also confirmed that antibodies generated against previous variants of the virus are much less effective against Omicron, but showed that recently boosted individuals have higher levels of effective antibodies. The research was published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States.

Ott and her colleagues studied the effect of different mutations in the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, and found that we may want to target other proteins than spike to generate better vaccines.
“The virus-like particle system lets us rapidly query new variants and get insight into whether their infectivity in cell culture is changed,” says Melanie Ott, MD, PhD, director of the Gladstone Institute of Virology and a senior author of the new study. “In the case of Omicron, it allowed us to get a much better handle on how, at a molecular level, this variant is different from others.”
“This approach is incredibly useful for quickly studying the effectiveness of prior antibodies and vaccines on a newly emerging viral strain,” says the study’s other senior author Jennifer Doudna, PhD, senior investigator at Gladstone, professor at UC Berkeley, founder of the Innovative Genomics Institute, and investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Virus-Like Particles Speed Omicron Research
Epidemiological data has suggested that the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, first detected in November 2021 in South Africa, spreads between people more easily than the original strain of the virus. Compared to other variants, it has also caused more breakthrough infections—in people previously infected with or fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
Early in 2021, Ott’s and Doudna’s research groups developed virus-like particles to study the SARS-CoV-2 virus. These particles are composed of the membrane, envelope, nucleocapsid, and spike proteins that make up the viral particle’s structure. However, virus-like particles lack the virus’s genome, so they cannot infect people and are therefore safer to work with than live virus. Scientists can also engineer new virus-like particles much faster than they can grow new variants of the live virus to study.

For this study, the team of researchers engineered virus-like particles, which are composed of the same proteins as the SARS-CoV-2 virus but lack its viral genome, so they are safer to work with than live virus. Shown here are Alison Ciling (left) and Abdullah Syed (right) working in a tissue culture room.
In their previous work, the researchers showed that the efficiency of virus-like particle assembly was related to the infectivity of the corresponding full, live virus. For instance, if a virus-like particle carrying a certain mutation was more efficient at forming viral particles, a copy of the live virus with the same mutation was also more infectious based on cell culture experiments.
In recent months, the team developed virus-like particles to capture the effect of different mutations in the emerging Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2.
Omicron mutations in the spike protein, they discovered, made virus-like particles twice as infectious as those with the ancestral spike protein. And virus-like particles carrying Omicron’s mutations in the nucleocapsid protein were 30 times more infectious than the ancestral SARS-CoV-2.
“There has been a lot of focus on spike, but we’re seeing in our system that for both Delta and Omicron, nucleocapsid is really more important in enhancing the spread of this virus,” says Ott. “I think if we want to generate better vaccines or look at blocking transmission of COVID-19, we might want to think about targets other than the spike protein.”
“We’re certainly not at a point where we fully understand this variant, but our data add to the growing evidence that it seems to be very good at infecting and very good at escaping antibodies.”
When the team made virus-like particles carrying Omicron mutations in the membrane or envelope proteins, they found that the particles were no more infectious than the ancestral virus-like particles; in fact, they were only about half as infectious as some other variants.
“Omicron has a lot of mutations, and our findings tell us that some of these mutations are actually harmful for the virus,” says Abdullah Syed, PhD, first author of the study and a postdoctoral fellow in Doudna’s lab at Gladstone. “But it also means that it could be possible for Omicron to evolve to be even more infectious if those brakes are lifted.”
How Omicron Escapes Antibodies
The researchers also tested the ability of antibodies to neutralize the SARS-CoV-2-like particles. They collaborated with the Innovation Team at Curative, which established a comprehensive serum biobank by administering over 2 million vaccinations across the US.
The team used serum of 38 people who had been vaccinated against COVID-19 or were unvaccinated but had recovered from the virus, as well as 8 people who had received a booster vaccine within the previous 3 weeks. Then, the researchers exposed the virus-like particles they had created to these serum samples to test their ability to neutralize the particles.
Sera from people vaccinated with the Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna vaccine within the previous 4 to 6 weeks showed high levels of neutralization against virus-like particles of ancestral SARS-CoV-2, but levels of neutralization were 3 times lower for particles of the Delta variant, and about 15 times lower for Omicron virus-like particles. People vaccinated with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine or who recovered from COVID-19 showed low levels of neutralization against the ancestral virus-like particles, and little difference was apparent for the Delta and Omicron variants.

Syed, the study's first author, helped improve our understanding of Omicron’s increased infectiousness and its escape from prior antibodies.
In addition, the researchers showed that within 2 to 3 weeks of receiving a third dose of Pfizer/BioNTech, all 8 boosted individuals in the study had detectable levels of antibodies capable of neutralizing all SARS-CoV-2 variants, including Omicron. However, levels of antibodies against Omicron were still 8 times lower than antibodies against the ancestral virus.
“Our findings support the idea that Omicron is much more capable of escaping our vaccine-induced immunity than previous strains of SARS-CoV-2,” says Ott. “It also underscores that booster shots from the mRNA vaccines seem to provide some degree of additional protection, even against Omicron.”
Additionally, when the team tested the monoclonal antibodies casirivimab and imdevimab (known commercially as REGEN-Cov), they found that the drugs showed high levels of neutralization against ancestral and Delta variants of SARS-CoV-2, but no detectable neutralization at all against the Omicron-like particles.
“We’re certainly not at a point where we fully understand this variant, but our data add to the growing evidence that it seems to be very good at infecting and very good at escaping antibodies,” says Syed.
For Media
Julie Langelier
Associate Director, Communications
415.734.5000
Email
About the Study
The paper “Omicron mutations enhance infectivity and reduce antibody neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles” was published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States on July 19, 2022.
Other authors are: Alison Ciling, Mir Khalid, Bharath Sreekumar, Renuka Kumar, Ines Silva, Taha Taha, Takako Tabata, and Irene Chen of Gladstone; and Bilal Milbes, Noah Kojima, Victoria Hess, Maria Shacreaw, Lauren Lopez, Matthew Brobeck, Fred Turner, and Lee Spraggon of Curative, Inc.
The work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R21AI59666 and F31AI164671-01), the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC PDF-533021-2019), the Roddenberry Foundation, and a gift from Pam and Ed Taft.
About Gladstone Institutes
Gladstone Institutes is an independent, nonprofit life science research organization that uses visionary science and technology to overcome disease. Established in 1979, it is located in the epicenter of biomedical and technological innovation, in the Mission Bay neighborhood of San Francisco. Gladstone has created a research model that disrupts how science is done, funds big ideas, and attracts the brightest minds.
Support Our COVID-19 Research Efforts
Gladstone scientists are moving quickly to respond to the coronavirus outbreak. Help us end this pandemic.
New Tool Reveals the Secrets of HIV-Infected Cells
New Tool Reveals the Secrets of HIV-Infected Cells
Developed by Gladstone scientists, HIV-seq could uncover new opportunities for treating HIV.
News Release Research (Publication) HIV/AIDS Infectious Disease Roan LabVitamin B3 Therapy Offers Hope for Fatal Childhood Disease
Vitamin B3 Therapy Offers Hope for Fatal Childhood Disease
A new framework that matches vitamins with genetic diseases helped uncover that high-dose vitamin B3 can dramatically extend survival in mice with NAXD deficiency.
News Release Research (Publication) Rare Diseases Jain LabGladstone Scientist Nadia Roan Elected to American Academy of Microbiology
Gladstone Scientist Nadia Roan Elected to American Academy of Microbiology
Roan has made great strides in understanding how persistent viruses including HIV cause disease and how immunity to viruses shapes human health.
Awards News Release COVID-19 HIV/AIDS Infectious Disease Roan Lab