The Stem Cell Core offers a fully functional tissue culture facility with specialized instruments, media, reagents, cell lines, and expertise for new or established researchers to perform cutting-edge stem cell research. In addition, our core provides comprehensive human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells–related training, consultations, and standard and customized scientific services, including derivation of iPS cells, differentiation of iPS cells and genome editing in iPS cells to stem cell researchers.
The Stem Cell Core partners with the Gladstone-CIRM Shared Resources Laboratory to offer a streamlined platform for stem cell-based disease modeling, drug screening, and CRISPR screening for therapeutic development.
Contact
Stem Cell Core Staff
Email
Services Provided
- iPS cell reprogramming from human fibroblasts and blood
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) isolated from whole human blood
- CRISPR-Cas9 mediated gene knock-in to safe harbor loci
- Differentiation of human iPS cells into cardiomyocytes
- Cell banking and distribution of human iPS cells and skin fibroblasts
- Training in human iPS cell culture, reprogramming and cardiac differentiation
- Standard quality control (mycoplasma screening, pluripotency, genetic stability)
- Consultations, collaborations, and educational seminars
Core Equipment
Cytiva NanoAssemblr Spark Nanoparticle Formulator
Integra ASSIST PLUS Machine
Bettersize Instruments BeNano 180 Zeta Pro Nanoparticle Characterizer
Invitrogen EVOS M5000 Imaging System
Echo Revolve Microscope
Cytiva NanoAssemblr Ignite Nanoparticle Formulator
Lonza 4D-Nucleofector 96-well Unit
Lonza 4D-Nucleofector Y Unit
Sartorius Incucyte S3 Live-Cell Analysis Machine
Interga VIAFLO 384 machine
EVOS FL Core Imaging System
Maestro Edge
Core Members
Sam Hu
Research Technologist I
Wendy Runyon
Research Scientist
The Stem Cell Core hosts a number of events from training to product demos.
Services Provided
The Stem Cell Core specializes in the generation, maintenance and differentiation of human iPS cells. The core has expertise in human iPS cell reprogramming and CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing of human iPS cells. The core supports researchers by providing the physical space, validated reagents, iPS cell lines and hands-on training for scientists to use iPS cells for their research goals.
Human iPS Cells Reprogramming
- iPS Cell Reprogramming from Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) (Episomal method)
- iPS Cell Reprogramming from Fibroblasts (ReproRNA StemCell Technologies Kit)
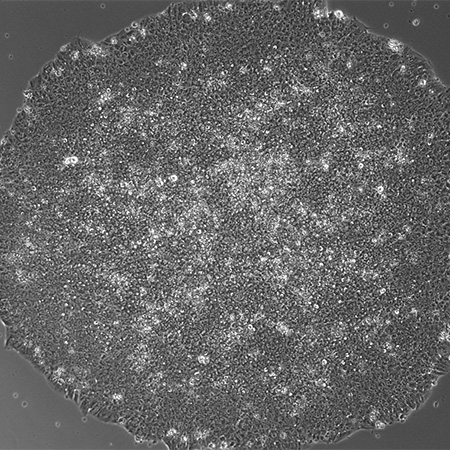
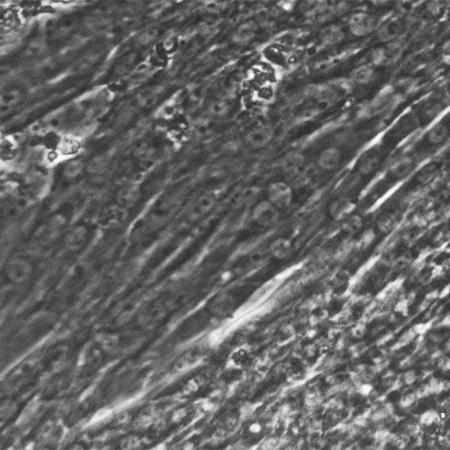
Cardiomyocyte Differentiation from Human iPS Cells
- Modulating Wnt Signaling
- StemCell Technologies Kit
Genome Engineering of Human iPS Cells
- CRISPR-Cas9 mediated gene knock-in to safe harbor loci (AAVS1 and CLYBL) for inserts such as, CRISPRi, NGN2 (cortical neuron), hNIL (lower motor neuron), NGN2-BRN3A (sensory neuron).


Training Services
- Human iPS Cells Culture and Maintenance
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation from Human iPS Cells
- Human iPS Cell Reprogramming from Fibroblasts and PBMCs
Supply of Cell Lines
- WTC-iPSC
- WTB-iPSC
- CRISPRi-iPSC
- CRISPRn-iPSC
- GCaMP6f-iPCS

Instrumentation
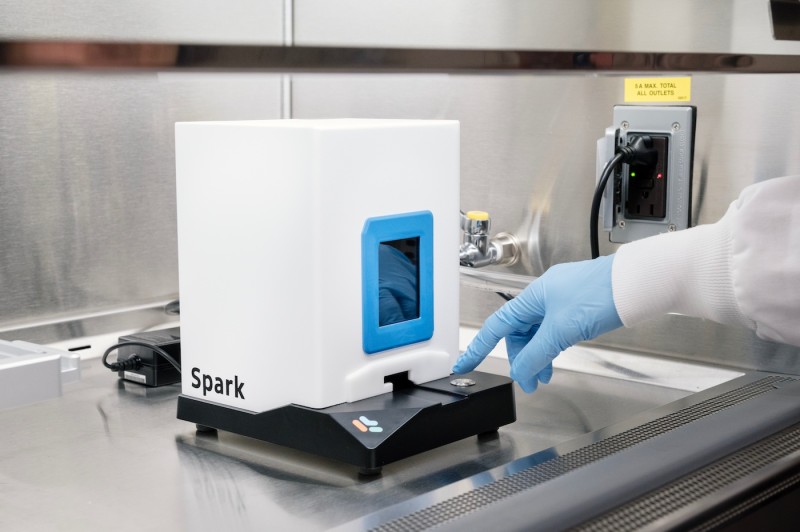

Cytiva NanoAssemblr Spark Nanoparticle Formulator
Applications
- Lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulation for delivering nucleic acid cargo (mRNA, siRNA, sgRNA, pDNA, etc.)
- Polymer nanoparticle, exosome, liposome, emulsion formulation
- Small scale production of nanoparticles for reproducible delivery screens
Specifications
- Microfluidic mixing instrument for formulating homogeneous nanoparticles of volume 25 – 250 μL
- Includes disposable cartridges with 2 input reservoirs to hold solutions in a 2:1 volume ratio
- 10 flow rate settings according to output volume
- Mixing time <30 seconds per nanoparticle formulation
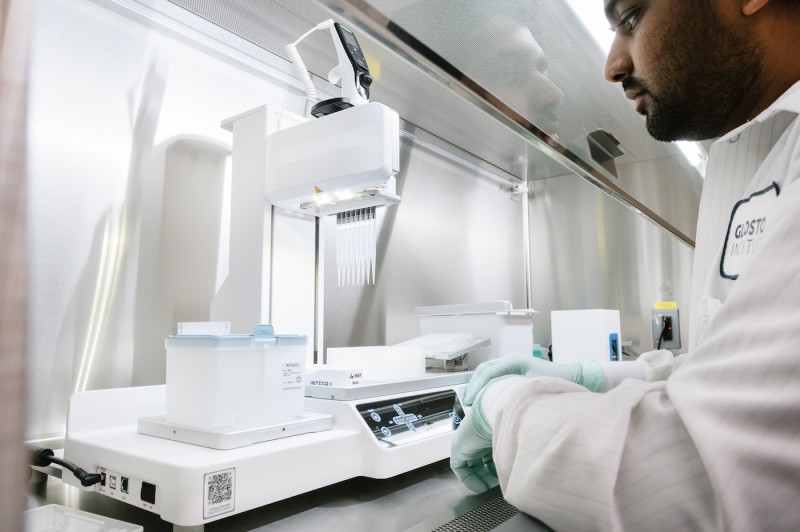

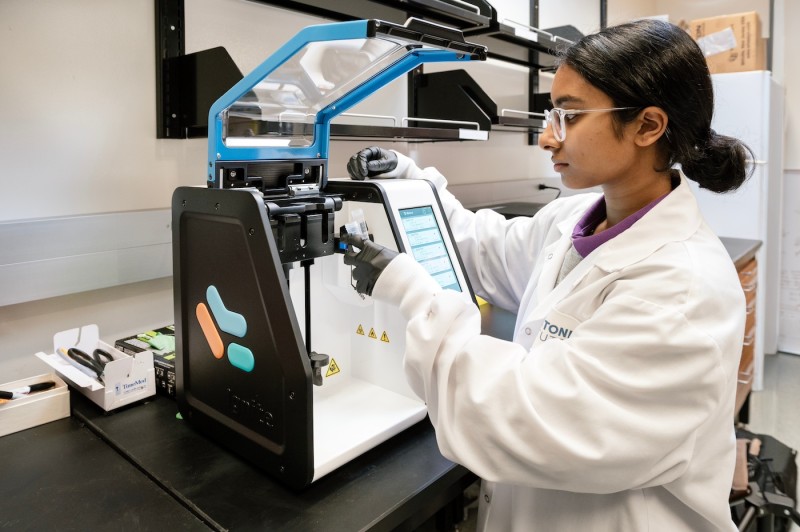
Integra ASSIST PLUS Machine
Applications
- Multi step cell culture protocols such as media changes and transfection
- Next generation sequencing sample cleanup
- Aliquot generation
- PCR setup
- ELISA automation
- High throughput arrayed screening of samples
Specifications
- Enables automated, multi-step sterile protocols for the aspiration, dispensing, and mixing of up to 384 samples simultaneously
- 5 unique spacing-adjustable pipettes with varying volume ranges (0.5 to 1250 µL) and channels (96 and 384)
- Pairs with VIALAB software to create, edit, simulate, and export automated protocols to pipettes
- 10°, 20°, 30° angled cell culture plate mount
- Customizable pipette speeds with adjustable vertical positioning
- Includes 3 deck positions
- 8x6 1.5mL Eppendorf tube rack
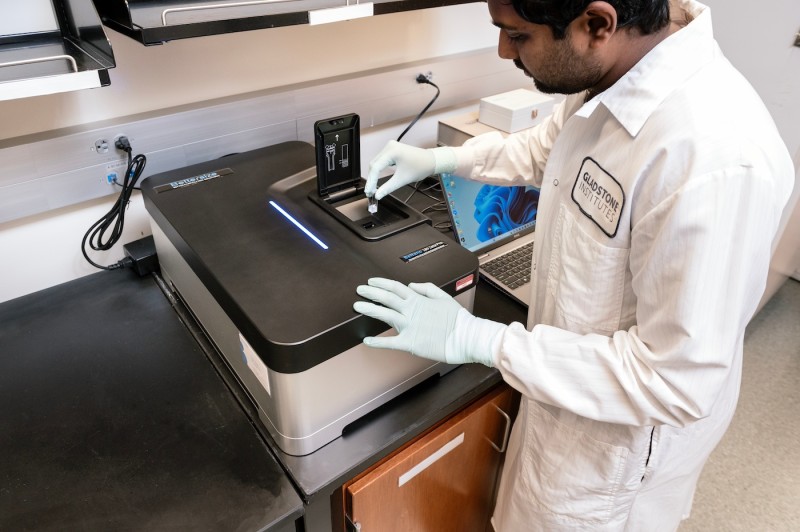

Bettersize Instruments BeNano 180 Zeta Pro Nanoparticle Characterizer
Applications
- Characterization of nanoparticle size distribution, stability, and surface structure
- Analysis of thermal-sensitive polymer systems
- Studying polymerization kinetics and reaction mechanisms
Specifications
- Dynamic light scattering (DLS), electrophoretic light scattering (ELS), and static light scattering (SLS) instrument
- Measures particle size in the range of 0.3nm – 15μm, zeta potential, and molecular weight
- Minimum sample volume: 3μL
- Programmable temperature control system
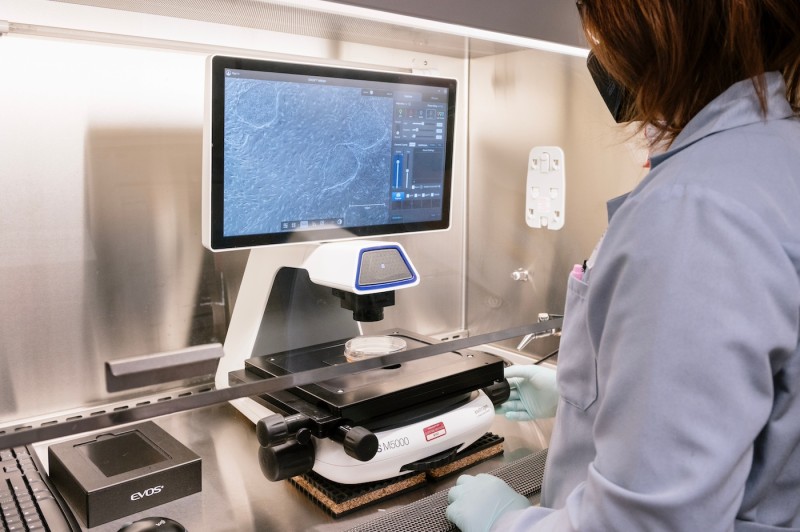

Invitrogen EVOS M5000 Imaging System
Specifications
- A fully integrated digital inverted microscope
- Designed for 3-color fluorescence (DAPI, GFP, RFP), transmitted-light, and color imaging
- Interchangeable optics, autofocus, and single-click multi-channel acquisition
- Offers post-capture tools such as brightness/contrast adjustments, annotations, and automated cell counting
- Includes autofocus, Z-stack capability and multi-channel capture
- On-board software for image acquisition, analysis, and cell counting
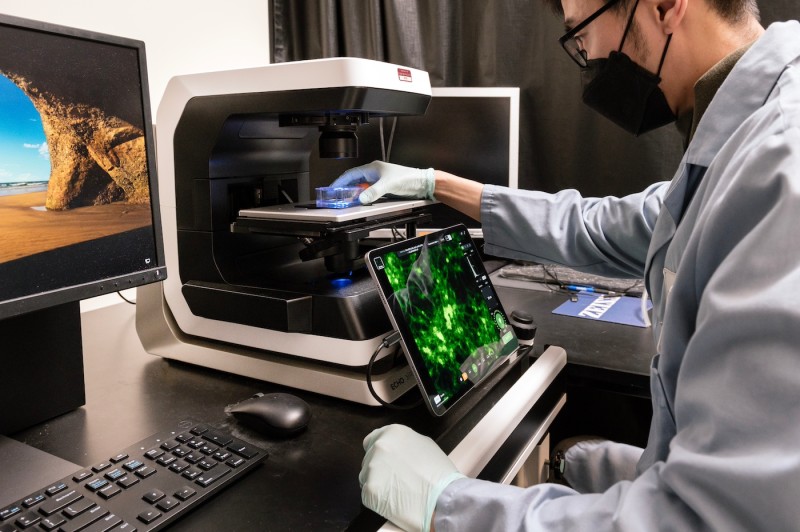

Echo Revolve Microscope
Specifications
- Hybrid microscope for upright and inverted observation methods
- 5 MP monochrome camera (upgraded from 3.2 MP) for enhanced field of view and fluorescence imaging resolution
- 5 MP CMOS color camera for brightfield imaging
- Intelligent objective nosepiece for automatic recognition of the objective being used
- iPad® tablet with retina display replaces traditional eyepieces for easier viewing
- Supports transmitted light, phase contrast, darkfield, polarized light, and fluorescence in both upright and inverted configurations
- Detects DAPI, FITC, TRITC Rhodamine and Texas Red

Cytiva NanoAssemblr Ignite Nanoparticle Formulator
Applications
- Lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulation for delivering nucleic acid cargo (mRNA, siRNA, sgRNA, pDNA, etc.)
Specifications
- Microfluidic mixing instrument for formulating homogeneous nanoparticles of volume 1 – 20 mL
- Includes disposable syringes to load input solutions
- Includes cartridges with 2 input mixing channels
- Variable flow rates (0.1 to 20 mL/min) and input volumes (<30 mL)
- Mixing time <2 min per nanoparticle formulation

Lonza 4D-Nucleofector 96-well Unit
Applications:
- Nucleofecting cells in 96-well format
- Testing multiple conditions for assay establishment<
- Screening cDNA, RNAi or CRISPR libraries
Specifications:
- Modular 6 × 16-well Nucleocuvette® Plate for scalable throughput
- Up to 96 independent programs can be run per plate, processed automatically in <2 minutes
- Compatible with many cell types including primary cells
- Variable cell numbers from 104–106 cells per reaction

Lonza 4D-Nucleofector Y Unit
Applications:
- Nucleofecting adhered cells in 24-well format
- Nucleofecting of cells at any time point during this culture period, i.e. at a later developmental stage
Specifications:
- Disposable conductive polymer Dipping Electrode Arrays are inserted into standard 24-well culture plates for Nucleofection
- Compatible with many cell types including primary cells
- Range of nucleofection conditions
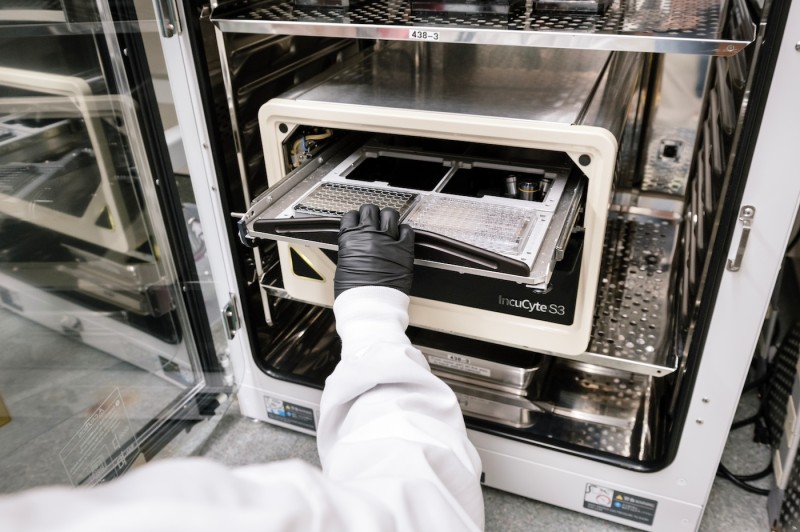

Sartorius Incucyte S3 Live-Cell Analysis Machine
Applications
- Monitoring of cells under various experimental conditions over time
- Fluorescence-based screening assays
Specifications
- Live cell imaging capacity of up to 6 cell plates within an incubator
- Two-color (red/green) fluorescence channels
- 4X, 10X, 20X objectives on an automated turret
- Compatible with over 700 cell culture vessels
- Remote cell monitoring capability
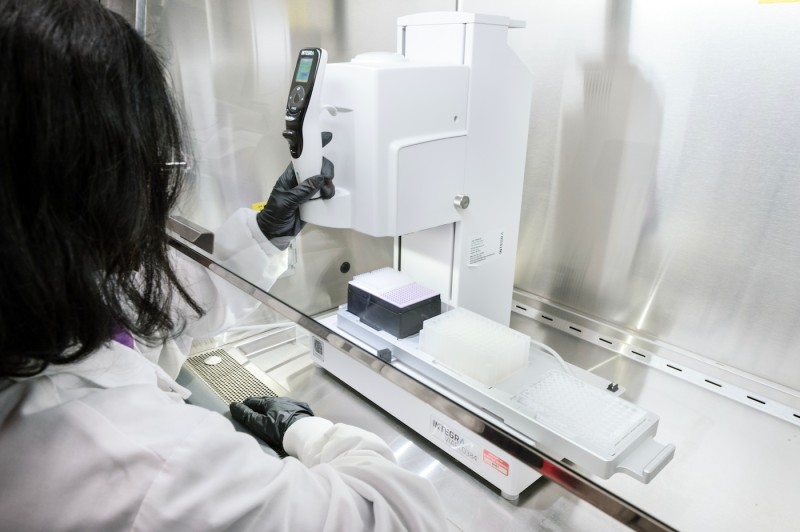

Interga VIAFLO 384 machine
Applications
- Expedited cell culture protocols
- Sample transfer
- PCR setup
- Sample extraction and purification
Specifications
- Enables sterile aspiration, dispensing, and mixing of up to 384 samples simultaneously
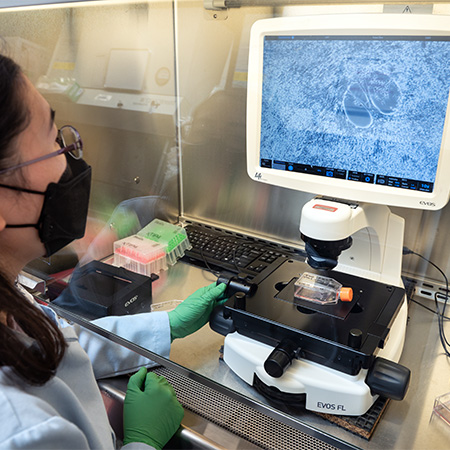

EVOS FL Core Imaging System
The EVOS FL is a comprehensive, high-performance fluorescence microscope crafted for both efficiency and user-friendliness. Its integrated onboard computer and imaging software enables users to directly capture, manage, and store multichannel fluorescence images and data from the microscope. This microscope is housed within a biosafety cabinet, making it well-suited for the picking of iPSC/ES colonies.
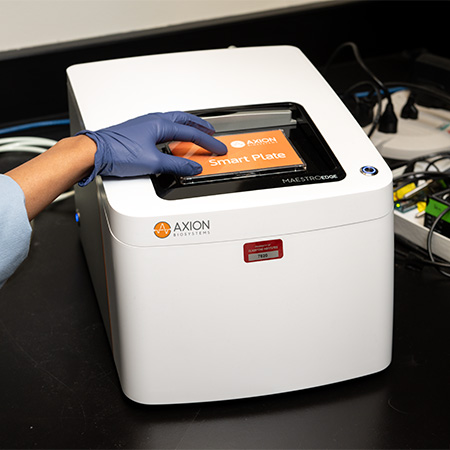

Maestro Edge
Maestro Edge MEA and Impedance system is ideal for low-throughput experiments. Record from 6- and 24-well MEA plates, plus 96-well impedance plates. Explore cell functionality easily in multiwell setups, whether tracking electrical activity or cell growth.
Fees and Scheduling
- Use of the Stem Cell Core facility is subject to fees charged as an add-on cost to in-house media purchased; alternatively, fees are charged via the purchase of a “sticker”. The add-on cost covers the use of plastics, PPE, some commonly used reagents, and standard equipment usage.
- Costs/fees for media, reagents, scientific services, and specialized equipment usage are listed on iLab. An iLab account is required to view specific pricing.
- The first 30-minute consultation is free of charge.
- For all fee inquiries or to set up an iLab account, email stemcell-core@gladstone.ucsf.edu.
- For custom scientific project inquiries or inquiries about use of specialized instruments, email stemcell-core@gladstone.ucsf.edu.
Scheduling
- To schedule new consultations and service requests, contact stemcell-core@gladstone.ucsf.edu. Once accepted, log into your Stem Cell Core iLab account and request the service.
- To schedule equipment use, visit iLab and book in the calendar.
Publications
Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Lines (RFSCi003-a, RFSCi004-A) From Monozygotic Twins Discordant for Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Rajendran N, Runyon W, Hu S, Singh A, Ratnapriya R, Kumar R, Csaky K, Sripathi SR. Stem Cell Res. 2025 Jul 5;87:103768. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2025.103768. PMID: 40627958.
Optimized, Efficient Measurement of the Expression of Undifferentiated Stem Cell Markers in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) by Flow Cytometry. Saware V, Runyon W, Hu S, van Soldt B, Kumar R, Srivastava J. Curr Protoc. 2025 Mar;5(3):e70105. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.70105. PMID: 40028708.
Functional Analysis of a Common BAG3 Allele Associated With Protection From Heart Failure. Perez-Bermejo JA, Judge LM, Jensen CL, Wu K, Watry HL, Truong A, Ho JJ, Carter M, Runyon WV, Kaake RM, Pulido EH, Mandegar MA, Swaney DL, So PL, Krogan NJ, Conklin BR. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2023 Jul;2(7):615-628. doi: 10.1038/s44161-023-00288-w. Epub 2023 Jun 26. PMID: 39195919.
Transcription Factor Protein Interactomes Reveal Genetic Determinants in Heart Disease. Barbara Gonzalez-Teran, Maureen Pittman, Franco Felix, Reuben Thomas, Desmond Richmond-Buccola, Ruth Hüttenhain, Krishna Choudhary, Elisabetta Moroni, Mauro W Costa, Yu Huang, Arun Padmanabhan, Michael Alexanian, Clara Youngna Lee, Bonnie E J Maven, Kaitlen Samse-Knapp, Sarah U Morton, Michael McGregor, Casey A Gifford, J G Seidman, Christine E Seidman, Bruce D Gelb, Giorgio Colombo, Bruce R Conklin, Brian L Black, Benoit G Bruneau, Nevan J Krogan, Katherine S Pollard, Deepak Srivastava. Cell 2022 Mar 3;185(5):794-814.
Brahma Safeguards Canalization of Cardiac Mesoderm Differentiation. Swetansu K Hota , Kavitha S Rao , Andrew P Blair , Ali Khalilimeybodi , Kevin M Hu , Reuben Thomas , Kevin So , Vasumathi Kameswaran , Jiewei Xu , Benjamin J Polacco , Ravi V Desai , Nilanjana Chatterjee , Austin Hsu , Jonathon M Muncie , Aaron M Blotnick , Sarah A B Winchester , Leor S Weinberger , Ruth Hüttenhain , Irfan S Kathiriya , Nevan J Krogan , Jeffrey J Saucerman , Benoit G Bruneau. Nature 2022 Feb;602(7895):129-134.
Transcription Factor GATA4 Regulates Cell Type-Specific Splicing Through Direct Interaction With RNA in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiac Progenitors. Lili Zhu, Krishna Choudhary, Barbara Gonzalez-Teran, Yen-Sin Ang, Reuben Thomas, Nicole R Stone, Lei Liu, Ping Zhou, Chenchen Zhu, Hongmei Ruan, Yu Huang, Shibo Jin, Angelo Pelonero, Frances Koback, Arun Padmanabhan, Nandhini Sadagopan, Austin Hsu, Mauro W Costa, Casey A Gifford, Joke G van Bemmel, Ruth Hüttenhain, Vasanth Vedantham, Bruce R Conklin, Brian L Black, Benoit G Bruneau, Lars Steinmetz, Nevan J Krogan, Katherine S Pollard, Deepak Srivastava. Circulation 2022 Sep 6;146(10):770-787.
Sars-Cov-2 Infection Of Human Ipsc-Derived Cardiac Cells Reflects Cytopathic Features in Hearts of Patients with Covid-19. Perez-Bermejo JA, Kang S, Rockwood SJ, Simoneau CR, Joy DA, Silva AC, Ramadoss GN, Flanigan WR, Fozouni P, Li H, Chen PY, Nakamura K, Whitman JD, Hanson PJ, McManus BM, Ott M, Conklin BR, McDevitt TC. Sci Transl Med 2021 Apr 21;13(590).
Allele-Specific Gene Editing Rescues Pathology in a Human Model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 2E. Feliciano CM, Wu K, Watry HL, Marley CBE, Ramadoss GN, Ghanim HY, Liu AZ, Zholudeva LV, McDevitt TC, Saporta MA, Conklin BR, Judge LM. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021 Aug 16;9:723023.
Transcription Factor Overexpression Drives Reliable Differentiation of Retinal Pigment Epithelium From Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Dewell TE, Gjoni K, Liu AZ, Libby ARG, Moore AT, So PL, Conklin BR. Stem Cell Res 2021 May;53:102368.
Sox2 and Klf4 as the Functional Core in Pluripotency Induction without Exogenous Oct4. An, Z., Liu, P., Zheng, J., et al. 2019. Cell Reports 29(7), p. 1986–2000.e8.
Differentiation of V2a interneurons from human pluripotent stem cells. Butts, J.C., McCreedy, D.A., Martinez-Vargas, J.A., et al. 2017. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 114(19), pp. 4969–4974.
Oligogenic inheritance of a human heart disease involving a genetic modifier. Gifford, C.A., Ranade, S.S., Samarakoon, R., et al. 2019. Science 364(6443), pp. 865–870.
BMP-SMAD-ID promotes reprogramming to pluripotency by inhibiting p16/INK4A-dependent senescence. Hayashi, Y., Hsiao, E.C., Sami, S., et al. 2016. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 113(46), pp. 13057–13062.
Miniaturized iPS-Cell-Derived Cardiac Muscles for Physiologically Relevant Drug Response Analyses. Huebsch, N., Loskill, P., Deveshwar, N., et al. 2016. Scientific Reports 6, p. 24726.
Automated Video-Based Analysis of Contractility and Calcium Flux in Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes Cultured over Different Spatial Scales. Huebsch, N., Loskill, P., Mandegar, M.A., et al. 2015. Tissue Engineering. Part C, Methods 21(5), pp. 467–479.
A BAG3 chaperone complex maintains cardiomyocyte function during proteotoxic stress. Judge, L.M., Perez-Bermejo, J.A., Truong, A., et al. 2017. Journal of Clinical Investigation Insight 2(14). PMC5518554
Spatiotemporal mosaic self-patterning of pluripotent stem cells using CRISPR interference. Libby, A.R., Joy, D.A., So, P.-L., et al. 2018. eLife 7.
CRISPR Interference Efficiently Induces Specific and Reversible Gene Silencing in Human iPSCs. Mandegar, M.A., Huebsch, N., Frolov, E.B., et al. 2016. Cell Stem Cell 18(4), pp. 541–553.
Isolation of single-base genome-edited human iPS cells without antibiotic selection. Miyaoka, Y., Chan, A.H., Judge, L.M., et al. 2014. Nature Methods 11(3), pp. 291–293.
Unbiased detection of CRISPR off-targets in vivo using DISCOVER-Seq. Wienert, B., Wyman, S.K., Richardson, C.D., et al. 2019. Science 364(6437), pp. 286–289.
The Cellular NMD Pathway Restricts Zika Virus Infection and Is Targeted by the Viral Capsid Protein. Fontaine, K.A., Leon, K.E., Khalid, M.M, Tomar, S., Jimenez-Morales, D., Dunlap, M., Kaye, J.A., Shah, P.S., Finkbeiner, S., Krogan, N.J., Ott. M. 2018. mBio. Nov-Dec; 9(6) PMCID: PMC6222128
Efficient CRISPR/Cas9-Based Genome Engineering in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Kime, C., Mandegar, M. A., Srivastava, D., Yamanaka, S., Conklin, B. R., & Rand, T. A. (2016). Current Protocols in Human Genetics, 88, 21.4.1–21.4.23.
Human disease modeling reveals integrated transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of NOTCH1 haploinsufficiency. Theodoris, C. V., Li, M., White, M. P., Liu, L., He, D., Pollard, K. S., Bruneau, B. G., & Srivastava, D. (2015). Cell, 160(6), 1072–1086.
FAQs
I would like to use the Stem Cell Core facility. How do I get started?
Contact us at stemcell-core@gladstone.ucsf.edu.
Do I Need a Service Contract for the Services?
All non-Gladstone investigators need a service contract for the services provided by the Stem Cell Core.
How Do I Pay For Services?
Consumables, services, and instrument usage are paid via iLab. We would set up an iLab account for you and you would submit a fund number (PO number) to order through your account.
Do You Provide Customized Services or Collaborations?
Yes, email stemcell-core@gladstone.ucsf.edu to discuss your project.
What Is the Wait Time for Scheduling My Project?
It depends on the project request and current workload of the Stem Cell Core. We generally require at least 2 weeks' notice to schedule new projects. Contact the core early to schedule your project.
Will I Have Access to My iPS Cell Cultures During Off-Peak Times?
You may be eligible for Gladstone badge access, which will give you access to the facility during off-peak times.
Do I Need a Material Transfer Agreement (MTA) for the iPSC Lines?
All non-Gladstone investigators require a Material Transfer Agreement for iPS cell lines provided by the Stem Cell Core.