The Assay Development and Drug Discovery Core provides in-house expertise coupled with state-of-the-art equipment to help academic and industry scientists establish new assays or adapt and refine existing ones for high-throughput screening, enabling target identification and drug discovery.
The core’s expertise applies to all life science disciplines to accelerate research into target and drug discovery phases, identify novel targets within pathways, and drive findings into clinical trials and ultimately therapies for disease.
For project advice, email Anke Meyer-Franke.
For equipment access, email Jane Srivastava.

Capabilities
Design
From the onset of a project, we take a flexible and collaborative approach. We will work with you directly to develop assays for your project or train you to develop, miniaturize, and optimize assays to be highly reproducible for medium (96-well) to high (384-well) throughput formats.

Build
Our team will assist in the iterative process required to test and optimize assay conditions, and can perform assays for you to save you time. Alternatively, we can train you to independently use plate readers for biochemical assays and use automated high-throughput microscopes for cell-based assays.

Automate
The core offers assistance and troubleshooting to automate screening assays that have been tested and validated on a small scale. We use robotic liquid handling systems to automate high-throughput assays and offer a fully bio-annotated library of compounds for screening.
Analyze and Inform
After automation, the core will run a small screen of compounds to validate the newly developed assay. After developing, optimizing, running and validating assays in-house, you can transfer these assays to high-throughput screening facilities (such as the Small Molecule Discovery Center at UC San Francisco) to perform additional screening with larger structurally diverse compound libraries.
Core Equipment
EL-406 Liquid Handler
Sector Imager
BioTek Synergy H4
Cellomics Arrayscan XTI
Meso Scale Discovery QuickPlex SQ120
Agilent BRAVO Benchcel system with PlateLoc Thermal Microplate Sealer
BioTek EL406 with plate stacker
BioTek MultiFlo FX in Biosafety cabinet
Molecular Devices ImageXpress Confocal HT.ai High-Content Imaging System
Thermo Scientific CellInsight CX7 Microscope
Services Provided
Consulting, Training, and Expert Advice
- Hourly access to state-of-the-art equipment
- Assistance to develop highly reproducible assays in 96- or 384-well plate formats
- Cell-based assays for high content imaging
- Biochemical assays (ELISAs, enzyme activity assays)
- Miniaturizing existing or developing new assays in 96-well plates
- Robust, highly reproducible assays with acceptable Z score
- Advice on image and data analysis
- Assistance with grant submissions and budgeting
Small Molecule Screen Optimization and Validation
- Expanding assay capability from 96- to 384-well format
- Automate process for screening purposes
- A bioannotated small molecule library, which combines:
- The SelleckChem library (2,100 compounds)
- The TargetMol library (3,071 compounds)
- The Microsource Spectrum library of bioactive compounds (2,400 compounds)
All three libraries have been used by others for drug discovery programs. The libraries contain FDA-approved drugs and compounds selected for neuroscience, ion channels, GPCRs, tyrosine kinases, membrane transporter/ion channel, microbiology, virology, immunology, and inflammation. Compounds are structurally diverse, medicinally active, and cell permeable. This library can be used for target and drug discovery, and for repurposing FDA-approved drugs.
Target Discovery
- Custom-designed screening in-house
- Collaboration with Gladstone’s Bioinformatics Core for pathway analysis
Drug Discovery
- Transfer of assay to high-throughput screening facility of collaborating organizations
- Design and perform secondary assays in-house
- Contacts to contract research organizations (CROs) and medicinal chemistry consultants
Equipment
Liquid Handling
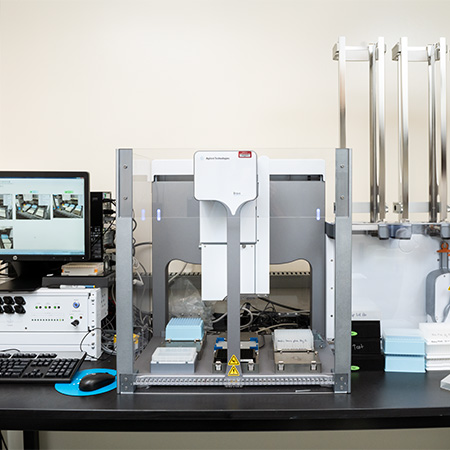



Agilent BRAVO Benchcel system with PlateLoc Thermal Microplate Sealer
Agilent BRAVO Benchcel system with PlateLoc Thermal Microplate Sealer
- 96 well pipette heads for small (ST: 1-70 µL) and larger (LT: up to 250 µL) volumes
- 9 decks including plate shaker
- 4 plate-stacking racks
Note: We use it for stamping library daughter plates, adding reagents to 96 or 384-well plates, making serial dilutions and the PlateLoc for thermally sealing microplates.
BioTek EL406 with plate stacker
- 96-well head to dispense and aspirate liquids
- Full plate washing and dispensing for ELISA assays and immunofluorescence staining for cell-based assays
- 8-channel cassettes manifold to dispense small amounts (minimum of 5 μL) of liquid. Note that the 8-channel cassette manifold is set at an angle to gently deliver small amounts of liquids for cell-based assays.
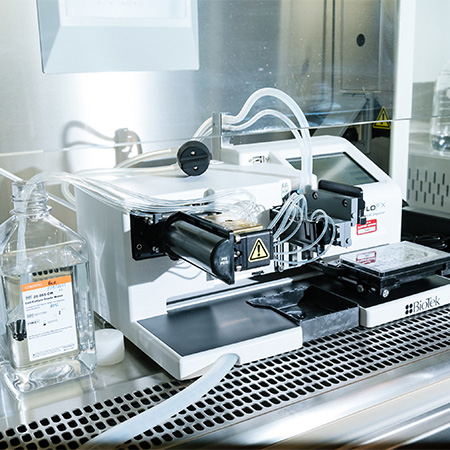
BioTek MultiFlo FX in Biosafety cabinet
Dispensing and aspirating liquids into 96 and 384 well plates in sterile environment with 8-channel cassettes
- Dispensing of cell suspensions
- Precoating of plates
Plate Readers
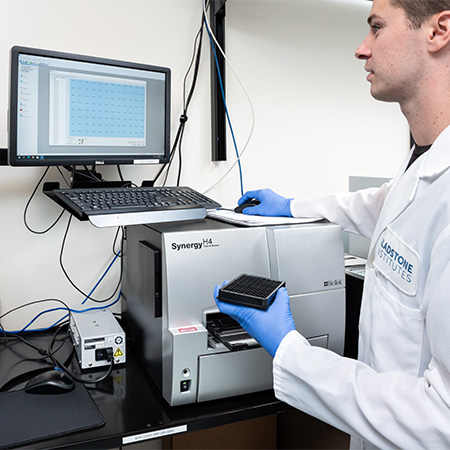


BioTek Synergy H4
- Colorimetric, fluorescence, and luminescence readouts
- 96 and 384-well microplates
Note: The plate reader is set for colorimetric, fluorescence and Luciferase assays. Fluorescence filters set up for Excitation 486/20, Emission 528/20 and Excitation 540/35, Emission 590/20.
Meso Scale Discovery QuickPlex SQ120
Electrochemiluminescence detection technology
Note: MSD offers assays that have ultra-low detection limits, provide up to five logs of linear dynamic range, use minimal sample and easily handle difficult matrices, including serum, plasma, urine, bronchoalveolar lavage, tissue and cell lysates, cell-supernatants, and CSF. The sensitivity and dynamic range enable the development of assays that can measure native levels of biomarkers in normal and diseased samples without multiple dilutions, saving time, resources, sample, and cost. The multiplex panels allow measurements of up to ten analytes from a single sample, MSD also offers off-the-shelf assays for biomarkers of inflammation, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular and metabolic dysfunction, and infectious diseases.
High-Content High-Throughput Microscopes
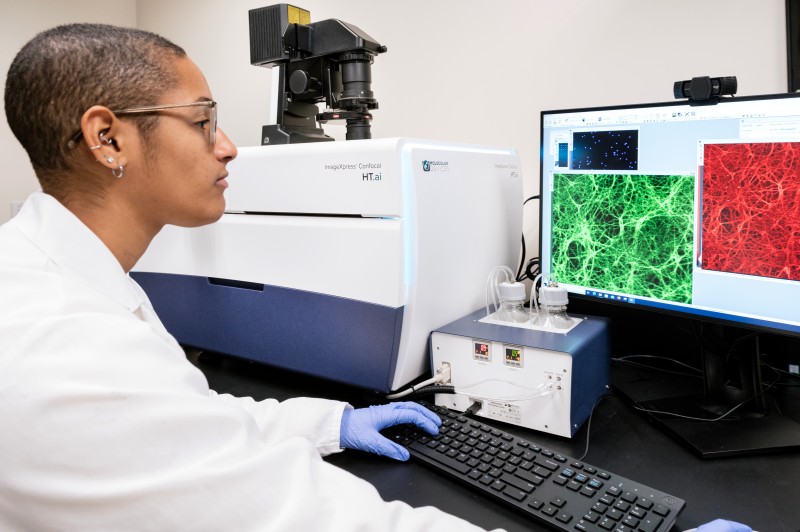


Molecular Devices ImageXpress Confocal HT.ai High-Content Imaging System
Applications
- Imaging 3D structures such as iPSC-derived neuronal cell clusters, iPSC-derived cells in matrigel and organoid cultures
- AI-based phenotypic analysis of iPSC-derived cell types
- Monitoring of cell health under various experimental conditions over time
- Fluorescence-based high throughput screening assays
Specifications
- 24, 48, 96 and 384-well formats
- Brightfield illumination
- Object-based and laser autofocus
- Live cell imaging capacity with incubator chamber
- 4,10, 20, 40 and 60x objectives
- 20x water immersion objective for greater resolution, faster imaging of subcellular structures
- In Carta image analysis software with large AI component for cell characterization
- 7 fluorescence channels and brightfield with an improved background to noise ratio
Thermo Scientific CellInsight CX7 Microscope
- Inverted microscope
- 96 and 384-well plate formats
- 7-LED light
- Imaging of four fluorescent channels
- 10, 20 and 40x Olympus objectives
- Brightfield illumination
- Powerful HCS Studio analysis software with built-in bioapplications such as Neuronal Profiling, allowing for tracing of neuronal processes
Notes: For optimal imaging we recommend tissue culture grade black walled plates with thin optical plastic. These plates are available from several companies, such as Corning (Falcon), Greiner, Nunc and Ibidi.
Once an analysis protocol has been set up in HCS Studio, image acquisition and analysis are running simultaneously.
Publications
Structure-dependent impairment of intracellular Apolipoprotein E4 trafficking and its detrimental effects are rescued by small molecule structure correctors. Brodbeck J, McGuire J, Liu Z, Meyer-Franke A, Balestra ME, Jeong D, Pleiss M, McComas C, Hess F, Witter D, Peterson S, Childers M, Goulet M, Liverton N, Hargreaves R, Freedman S, Weisgraber K, Mahley RW and Huang Y (2011) JBC, 286(19):17217–26
Small molecule structure correctors abolish detrimental effects of apolipoprotein E4 in cultured neurons. Chen HK, Liu Z, Meyer-Franke A, Brodbeck J, Miranda RD, McGuire JG, Pleiss MA, Ji ZS, Balestra ME, Walker DW, Xu Q, Jeong DE, Budamagunta MS, Voss JC, Freedman SB, Weisgraber KH, Huang Y, Mahley RW (2012) JBC, 287(8):5253-66
Blood coagulation protein fibrinogen promotes autoimmunity and demyelination via chemokine release and antigen presentation. Ryu JK, Petersen MA, Murray SG, Baeten KM, Meyer-Franke A, Chan JP, Vagena E, Bedard C, Machado MR, Rios Coronado PE, Prod’homme T, Charo IF, Lassmann H, Degen JL, Zamvil SS & Akassoglou K (2015) Nat. Commun. 6:8164
Scalable Production of iPSC-Derived Human Neurons to Identify Tau-Lowering Compounds by High-Content Screening. Wang C, Ward ME, Chen R, Liu K, Tracy TE, Chen X, Xie M, Sohn PD, Ludwig C, Meyer-Franke A, Karch CM, Ding S, Gan L. (2017) Stem Cell Reports, 9(4):1221–1233
Fibrinogen activates BMP signaling in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and inhibits remyelination after vascular damage. Petersen MA, Kyu Ryu J, Chang K-J, Etxeberria A, Bardehle S, Mendiola A, Kamau-Devers W, Fancy SPJ, Thor A, Bushong EA, Baeza-Raja B, Syme CA, Wu MD, Rios Coronado PE, Meyer-Franke A, Yahn S, Pous L, Lee JK, Schachtrup C, Lasman H, Huang EJ, Han MH, Absinta M, Reich D, Ellisman MH, Rowitch DH, Chan JR and Akassoglou K (2017) Neuron, 96:1–10
Fibrin-targeting immunotherapy protects against neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Ryu JK, Rafalski VA*, Meyer-Franke A*, Adams RA, Poda SB, Rios Coronado PE, Pedersen LØ, Menon V, Baeten KM, Sikorski SL, Bedard C, Hanspers K, Bardehle S, Mendiola AS, Davalos D, Machado MR, Chan JP, Plastira I, Petersen MA, Pfaff SJ, Ang KK, Hallenbeck KK, Syme C, Hakozaki H, Ellisman MH, Swanson RA, Zamvil SS, Arkin MR, Zorn SH, Pico AR, Mucke L, Freedman SB, Stavenhagen JB, Nelson RB, Akassoglou K. (2018) Nat. Immunol., 19:1212–223
Transcriptional profiling and therapeutic targeting of oxidative stress in neuroinflammation. Mendiola AS, Ryu JK, Bardehle S, Meyer-Franke A, Ang KK, Wilson C, Baeten KM, Hanspers K, Merlini M, Thomas S, Petersen MA, Williams A, Thomas R, Rafalski VA, Meza-Acevedo R, Tognatta R, Yan Z, Pfaff SJ, Machado MR, Bedard C, Rios Coronado PE, Jiang X, Wang J, Pleiss MA, Green AJ, Zamvil SS, Pico AR, Bruneau BG, Arkin MR, Akassoglou K. (2020) Nat. Immunol., 21: 513–524






